반응형
클래스
- 객체지향 프로그래밍 (OOP)
- 객체지향 프로그래밍의 특징
- 상속 : 부모/자식
- 캡술화 (encapsulation), 정보 은닉
- 보안 (secure)
- 안전 (safe)
- 사용성 (useful)
- 다형성 (polymophism)
- 여러 자료형을 가질 수 있는 성질 → 하나의 실행문으로 다른 결과 도출
- 클래스 (설계도) - 객체 (피조물)
- 객체 생성
- 자료형 변수명 = 값
- 클래스 변수명 = new 클래스 () → 객체가 나옴
- 클래스의 용도
- 타입(종류) classification
- 데이터 저장 (자료 구조)
- 기능 보관 (파일, 폴더)
- 생성자가 없다면 자바가 컴파일 시간에 기본 생성자 자동으로 생성
- 기본 생성자 = 매개변수가 없는 생성자
- 생성자를 만들어 줄 때에는, 변수명은 기재하지 않는다.
- 리턴 타입이 없다.
- 이름이 클래스명과 동일해야 한다.
- Student() { }
- 만약 매개변수 생성자 (직접 만든 생성자)가 있을 경우, 기본 생성자를 선언하지 않고 사용 시 오류
- 오버로딩 (Overloading) 이라고 한다.
- package ch06.sec07.exam01; public class Car { Car(String name, String color, int maxSpeed) { } } package ch06.sec07.exam01; public class CarExam { static void main(String[] args) { Car myCar = new Car("그랜저","검정",250); //Car myCar = new Car() // 기본 생성자는 호출하지 못함 } }
- 오버로드 (Over + load)
- 이름이 같고, 매개 변수의 순서나 타입이 달라지는 것
- 중복되는 함수의 경우 모두 구현 해주어야 함
- ≠ 오버라이드
- 오버라이드
- 부모의 메소드를 자식에서 다시 재정의 하는 것
- this
- 나 자신을 가리키는 객체
- 해당 객체의 필드를 구분
- this를 이용하여 공통 코드를 가지고 있는 생성자를 호출하면 중복 코드를 줄일 수 있음
- 변환 전
package ch06.sec07.exam01; public class Car { private String model; private String color; private int maxSpeed; Car(String model){ this.model = model; this.color = "은색"; this.maxSpeed = 250; System.out.println(this.model + ", " + this.color + ", " + this.maxSpeed); } Car(String model, String color){ this.model = model; this.color = color; this.maxSpeed = 250; System.out.println(this.model + ", " + this.color + ", " + this.maxSpeed); } Car(String model, String color, int maxSpeed) { this.model = model; this.color = color; this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed; System.out.println(this.model + ", " + this.color + ", " + this.maxSpeed); } }- 변환 후
package ch06.sec07.exam01; public class Car { private String model; private String color; private int maxSpeed; Car(String model){ this(model, "은색", 250); } Car(String model, String color){ this(model, color, 250); } Car(String model, String color, int maxSpeed){ this.model = model; this.color = color; this.maxSpeed = maxSpeed; System.out.println(this.model + ", " + this.color + ", " + this.maxSpeed); } }
Static
- static 키워드가 붙어있지 않다면 인스턴스 필드 (클래스 내부 필드)
- static은 객체를 생성하지 않아도 메모리에 로드되어 사용 가능
- 클래스 이름으로 접근해도 되고, 객체의 이름으로 접근해도 됨 (확실하게 공유하는 것을 보여주기 위해 클래스 이름으로 접근하는 것을 권유)
- instance : 객체.멤버
- class : 클래스.멤버 (공유)
- 많이 사용하면 메모리를 많이 잡아먹음 (객체를 생성하지 않아도 메모리를 점유)
// static 블록 (처음 1회만 실행) static { System.out.println("static 블록"); } // instance 블록 (객체를 생성할 때마다 실행) { System.out.println("instance 블록"); } 객체 생성 시 실행 결과 --------------------------------- static 블록 instance 블록
- instance vs static
- static
- 정적/고정
- 메모리 로드
- 클래스를 통해 사용
- instance
- 객체를 통해 사용
- static
final
- 마지막
- 필드
- 마지막 필드 (상수 : static final)
- 초깃값이 저장되면 더 이상 수정 불가
- 메서드
- 재정의 불가 (= 메소드 오버라이드 불가)
- 클래스
- 상속 불가
- String 클래스는 상속 불가
- 상수
- static final로 쓸 수 있다.
- 패키지
- 폴더(디렉토리)
- 클래스 명
- 패키지 포함
- ex) java.lang.String
- 클래스 명
- 폴더(디렉토리)
필드, 메서드
public class Student {
String name; // 필드
void method1() {
String name = null; // 지역 변수
System.out.println(name); // 변수 출력
System.out.println(this.name); // 필드 출력
}
void method2() {
System.out.println(name); // 필드 출력
}
}
메서드
- 메서드 중첩
- 메서드1( 메서드2( 메서드3 ) ) )일 경우 실행 순서는 1→2→3
- 끝나는 순서는 3→2→1
- 출력은 끝나는 구조
- 스택 자료 구조와 비슷
- 리턴
- 메서드를 실행한 곳으로 돌아감 (값을 가지고 가거나, 그냥)
- 메서드 실행 중지 용도로 사용 가능
- 선언부 : 접근제한자 [static] 자료형 메서드 명 ([매개 변수])
- Return
- 나를 실행한 곳으로 돌아감
- 값을 가지고 돌아감
package ch06.sec08.exam03; public class Car { int gas; void setGas(int gas) { this.gas = gas; } boolean isLeftGas() { if(gas==0) { System.out.println("gas가 없습니다"); return false; } System.out.println("gas가 있습니다."); return true; } void run() { while(true) { if(gas > 0) { System.out.println("달립니다.(gas잔량:" + gas + ")"); gas -= 1; }else { System.out.println("멈춥니다.(gas잔량:" + gas + ")"); return; } } } } package ch06.sec08.exam03; public class CarExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Car myCar = new Car(); myCar.setGas(5); if (myCar.isLeftGas()) { System.out.println("출발합니다."); myCar.run(); } System.out.println("gas를 주입하세요."); } } 실행 결과 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- gas가 있습니다. 출발합니다. 달립니다.(gas잔량:5) 달립니다.(gas잔량:4) 달립니다.(gas잔량:3) 달립니다.(gas잔량:2) 달립니다.(gas잔량:1) 멈춥니다.(gas잔량:0) gas를 주입하세요.
패키지
- 패키지가 없으면 default 패키지
- 이 방법은 사용하지 않는 것이 좋음
- 이미 존재하는 패키지명은 사용하면 안됨
접근 제한자
- public
- 전체 (다른 패키지에서도 접근 가능)
- protected
- 같은 패키지에서만 + 상속
- default
- 없는 것 (같은 패키지에서만)
- private
- 현재 클래스 안에서만
- 범위
- private < default < protected < public
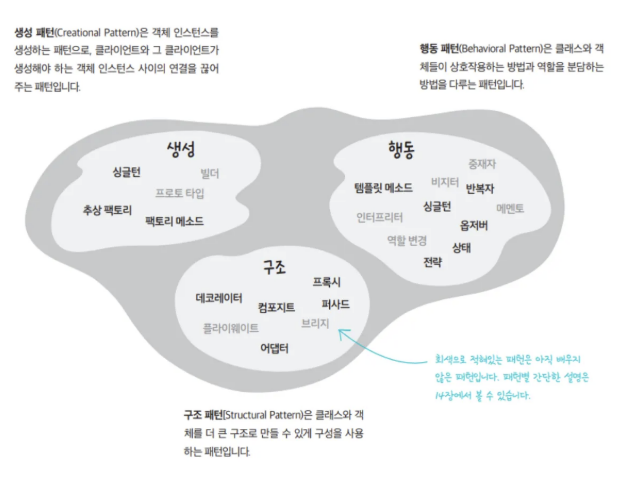
싱글톤 패턴
- 앱 전체에서 단 한개의 객체만 생성, 사용하는 것
- 디자인패턴 중 하나
- 객체가 생성되기 전에 메모리에 올라감
package ch06.sec15; public class Singleton { private static Singleton singleton = new Singleton(); // 싱글톤 객체가 저장되어 있는 메모리의 주소값 private Singleton() {} public static Singleton getInstance() { return singleton; // 주소값 리턴 } } package ch06.sec15; public class SingletonExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Singleton obj1 = new Singleton(); // 에러 // Singleton obj2 = new Singleton(); // 에러 Singleton obj1 = Singleton.getInstance(); Singleton obj2 = Singleton.getInstance(); if(obj1 == obj2) { System.out.println("같은 객체"); } else { System.out.println("다른 객체"); } } } 출력 결과 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 같은 객체
메모
- 이클립스는 자체적으로 변수와 필드의 색깔을 구분해준다.
- 다크모드 기준 : 필드는 파랑, 지역 변수는 노랑
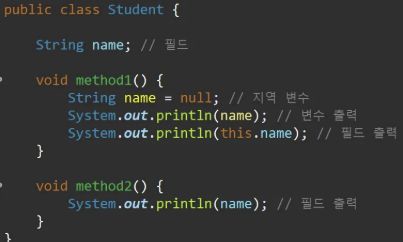
- 지역 변수는 내가 실행하는 코드보다 밑에 있을 수 없음
- 반올림
- Math.round(3.5)
- 자동 get, set 생성
- source > generate getters and setters > select all > generate
- alt + shift + s > r > alt + a > alt + r
- 패키지는 풀네임 모두 기재
- 스프링프레임워크에서 클래스의 풀네임을 기재해야함
- 문서에서 [ ]는 생략 가능하다는 것을 의미
- 디자인 패턴은 약 23개가 있지만, 가장 많이 쓰이는 것은 GOF 디자인 패턴
728x90
반응형
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4/9 - 라이브러리와 모듈, 예외 처리, java.base 모듈 (1) (1) | 2025.04.12 |
|---|---|
| 4/8 - 상속, 인터페이스, 중첩 선언과 익명 객체 (0) | 2025.04.12 |
| 이것이 자바다 - 챕터5 연습 문제 (0) | 2025.04.05 |
| 이것이 자바다 - 챕터4 연습 문제 (0) | 2025.04.05 |
| 이것이 자바다 - 챕터3 연습 문제 (0) | 2025.04.05 |
